Stablecoin: A Comprehensive Guide
What Are Stablecoins?
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies whose value is pegged, or tied, to that of another currency, commodity, or financial instrument. They are designed to maintain a stable value relative to a specified asset, or a pool or basket of assets. Unlike highly volatile cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, stablecoins aim to provide an alternative that combines the technological benefits of blockchain with the stability of traditional financial assets.
The primary purpose of stablecoins is to address the volatility problem that makes other cryptocurrencies less suitable for everyday transactions. By maintaining a relatively stable value, they serve as a bridge between traditional financial systems and the digital economy.
How Do Stablecoins Work?
Stablecoins typically go through several stages before users can utilize them. First, a company issues a stablecoin, and for every stablecoin it issues, the company also holds the same value in a country's currency or other backing assets. The stablecoin is then issued to the broader public through blockchain infrastructure that records transactions and transfers value between individuals.
The value of the stablecoin issued onto the ledger is linked to the stable assets that the issuer holds, meaning coin-holders can exchange their stablecoins for money in their existing bank accounts easily and without loss. Users access their stablecoins through digital wallets, which can be used on smartphones or other hardware and software to store, send, and receive their coins.
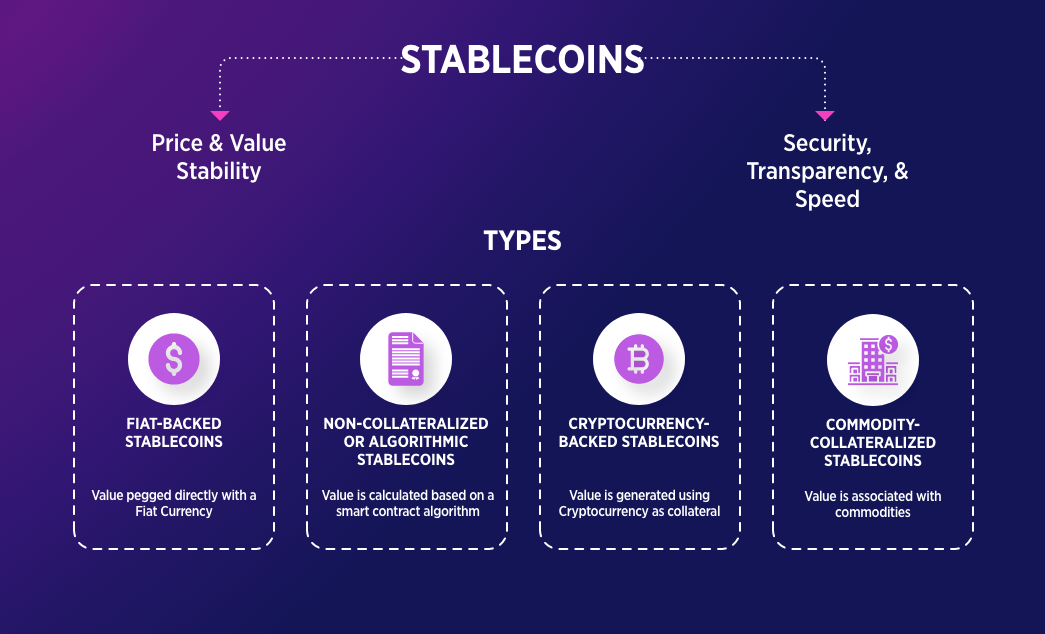
Types of Stablecoins
Fiat-Collateralized Stablecoins
Fiat-collateralized stablecoins maintain a reserve of a fiat currency, such as the U.S. dollar, as collateral, assuring the stablecoin's value. These reserves are maintained by independent custodians and are regularly audited. Popular examples include Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC), which are backed by U.S. dollar reserves and denominated at parity to the dollar.
Crypto-Collateralized Stablecoins
Crypto-collateralized stablecoins are backed by other cryptocurrencies. Because the reserve cryptocurrency may also be prone to high volatility, such stablecoins are generally overcollateralized—meaning the value of cryptocurrency held in reserves exceeds the value of the stablecoins issued. For example, MakerDAO's Dai (DAI) stablecoin is pegged to the U.S. dollar but is backed by Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies worth about 155% of the DAI stablecoin in circulation.
Algorithmic Stablecoins
Algorithmic stablecoins may or may not hold reserve assets, but their primary distinction is the strategy of keeping the stablecoin's value stable by controlling its supply through an algorithm. These stablecoins use software algorithms to automatically adjust the supply based on demand, aiming to maintain a stable price. However, this type has faced significant challenges, as demonstrated by the collapse of TerraUSD (UST) in 2022.
Commodity-Backed Stablecoins
Commodity-backed stablecoins are pegged to the market value of commodities such as gold, silver, or oil. These stablecoins generally hold the commodity using third-party custodians or by investing in instruments that hold them. One popular example is Tether Gold (XAUt), a cryptocurrency backed by gold reserves.
Popular Stablecoins
The most widely-used stablecoins by market capitalization and trading volume are USDT, USDC, and DAI. As of June 2025, Tether (USDT) had a market cap of $153.4 billion, while USD Coin (USDC) had $61.1 billion. These stablecoins dominate the market, with the total stablecoin market capitalization reaching an all-time high of $204 billion in 2025.
Key Use Cases
Cross-Border Payments and Remittances
Stablecoins cut out intermediaries, allowing users to send money across borders instantly and at a fraction of the cost of traditional systems. For example, a freelancer in Argentina working for a European company can receive payments in USDC within minutes, without currency exchange or bank delays.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Applications
Stablecoins are foundational to DeFi platforms, where users can lend and earn interest, borrow against crypto collateral without selling assets, provide liquidity in decentralized exchanges, and participate in yield farming. Platforms such as Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO enable users to borrow stablecoins against crypto collateral while lenders earn interest on their deposits.
Business Payments
Companies are using stablecoins for payroll and B2B transactions, particularly for paying remote employees and contractors across borders. This reduces transaction fees and speeds up disbursements, improving cash flow for workers. SpaceX utilizes stablecoins to collect payments from Starlink customers in countries with underdeveloped financial systems.
E-Commerce and Merchant Payments
Stablecoins enable real-time settlements for online businesses, allowing merchants to accept payments and receive value immediately without worrying about delayed bank transfers or crypto volatility. This is especially valuable in regions with underdeveloped banking systems or unstable local currencies.
Advantages of Stablecoins
Stablecoins offer several compelling benefits for users and businesses:
Price Stability: They maintain consistent value, providing a dependable method for money storage and transactions
Fast, Low-Cost Transactions: Stablecoins provide swift and affordable payment processing, operating 24/7 unlike traditional banking systems
Global Accessibility: They facilitate cross-border transactions without currency conversions or intermediaries
Programmability: Can be integrated into smart contracts and automated payment systems
Financial Inclusion: Offer access to digital dollars for users in unstable economies or underbanked regions without requiring bank accounts
Risks and Disadvantages
Despite their benefits, stablecoins come with several risks and limitations:
De-pegging Risk
Market fluctuations, loss of confidence, or liquidity issues can cause a stablecoin to deviate from its intended peg. The most notable example was the collapse of TerraUSD (UST) in 2022, which lost its dollar peg and crashed more than 60%.
Centralization and Counterparty Risk
Many stablecoins are issued by centralized entities that control backing assets and the issuance process. Users must trust that issuers maintain sufficient reserves and operate sustainably. The largest reserve-backed stablecoins retain the sole prerogative to mint and destroy tokens.
Reserve Management
For fiat-collateralized stablecoins, the management and auditing of reserve assets are critical. Poor management, lack of transparency, or fraudulent behavior by issuers can undermine stability. Some companies have faced challenges in providing adequate proof that valid audits fully back their reserves.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The global regulatory environment continues to evolve, creating uncertainties for stablecoin protocols. Regulatory scrutiny is increasing as the market grows and its potential to affect the broader financial system becomes more apparent.
Regulatory Developments
In June 2025, the U.S. Senate passed the GENIUS Act, which aims to establish a regulatory framework for stablecoins for the first time. The legislation garnered bipartisan support with a 68-30 vote and would require stablecoins to be backed by liquid assets and mandate monthly public disclosure of reserve compositions.
Market Growth and Future Outlook
The stablecoin market has experienced significant growth, with global supply increasing by 63% between February 2024 and February 2025. During this period, stablecoins facilitated more than $35 trillion in transfers, with monthly transfer volume doubling. Established financial firms are demonstrating increased interest, with Stripe acquiring Bridge for $1.1 billion and PayPal introducing its own stablecoin.
Stablecoins represent more than two-thirds of the trillions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency transactions recorded in recent months. They are gaining momentum as both a medium of exchange and store of value, addressing gaps left by traditional currencies, particularly in regions with monetary instability and limited access to the U.S. dollar.
Conclusion
Stablecoins have emerged as a crucial component of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, offering the technological benefits of blockchain while addressing the volatility concerns that limit the practical use of other cryptocurrencies. While they present significant opportunities for financial innovation, users and businesses must carefully consider the associated risks, including de-pegging, centralization, and regulatory uncertainties. As the regulatory framework develops and technology matures, stablecoins are positioned to play an increasingly important role in the future of digital finance.
Sources:
Coinbase. (2024, April 2). What is a stablecoin? Coinbase Learn. https://www.coinbase.com/learn/crypto-basics/what-is-a-stablecoin
Fernando, J. (2024, June 13). Stablecoins: Definition, how they work, and types. Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/stablecoin.asp
Wikipedia. (2018, May 17). Stablecoin. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stablecoin
Kansas Legislative Research Department. (2024, November 15). Stablecoin overview. KLRD. https://klrd.gov/2024/11/15/stablecoin-overview/
Modern Treasury. (2020, November 16). What is a stablecoin? Modern Treasury Learn. https://www.moderntreasury.com/learn/what-is-a-stablecoin
Trust Machines. (2023, August 7). Two types of crypto stablecoins: Fiat vs. algorithm-backed coins. Trust Machines Blog. https://trustmachines.co/blog/crypto-stablecoins-fiat-vs-algorithm-backed-coins/
Gate.io. (2025, May 28). What will be the market capitalization of USDC in 2025? Analysis of the stablecoin market landscape. Gate.io. https://www.gate.io/crypto-wiki/article/what-will-the-usdc-market-value-be-in-2025
TokenMinds. (2025, June 12). Power of DeFi: How cross-border payments are getting faster & cheaper. TokenMinds Blog. https://tokenminds.co/blog/knowledge-base/power-of-defi
The Block. (2023, December 11). What are the different types of stablecoins? The Block Learn. https://www.theblock.co/learn/251859/the-different-types-of-stablecoins-explained
Lowe, S. (2025, June 18). Trump crypto czar calls GENIUS Act passage a landmark moment for stablecoin regulation. The Crypto Basic. https://thecryptobasic.com/2025/06/18/trump-crypto-czar-calls-genius-act-passage-a-landmark-moment-for-stablecoin-regulation/
Rennison, J. (2025, June 17). U.S. Senate passes GENIUS Act to regulate stablecoins, marking crypto industry win. CoinDesk. https://www.coindesk.com/policy/2025/06/17/u-s-senate-passes-genius-act-to-regulate-stablecoins-marking-crypto-industry-win
Tron Weekly. (2025, June 18). Stablecoin regulation gains momentum as US Senate approves GENIUS Act. Tron Weekly. https://www.tronweekly.com/stablecoin-regulation-gains-momentum-as-us/
PYMNTS. (2025, June 18). GENIUS Act rides stablecoin momentum as Senate clears path for crypto regulation. PYMNTS. https://www.pymnts.com/cryptocurrency/2025/u-s-senate-passes-genius-act-stablecoin-regulations-in-crypto-first/
Berkeley Institute for People and Culture. (2025, June 19). The GENIUS Act and its impact on the future of stablecoins. BIPC. https://www.bipc.com/the-genius-act-and-its-impact-on-the-future-of-stablecoins
Blockchain News. (2025, March 24). Tether USDT growth projection to 2025 and beyond. Blockchain News Flash. https://blockchain.news/flashnews/tether-usdt-growth-projection-to-2025-and-beyond
BlockApps. (2024, December 26). What caused the depeg of TerraUSD? An in-depth analysis of its collapse. BlockApps Blog. https://blockapps.net/blog/what-caused-the-depeg-of-terrausd-an-in-depth-analysis-of-its-collapse/
CCN. (2024, October 21). Stripe's $1.1B Bridge acquisition among crypto's largest. CCN. https://www.ccn.com/news/crypto/stripe-in-negotiations-to-acquire-stablecoin-fintech-firm-bridge/
Blockchain News. (2025, May 12). Tether USD₮ hits $150B milestone: Stablecoin growth drives crypto trading liquidity in 2025. Blockchain News Flash. https://blockchain.news/flashnews/tether-usd-hits-150b-milestone-stablecoin-growth-drives-crypto-trading-liquidity-in-2025
Murugaboopathy, P. (2025, June 18). Stablecoin just hit a record $252 billion market cap. Inc. Magazine. https://www.inc.com/reuters/stablecoin-record-market-cap-senate-genius-act-crypto-regulation-bill/91203413
AInvest. (2025, June 12). Stablecoin market capitalization surges 17% to $228 billion in 2025. AInvest News. https://www.ainvest.com/news/stablecoin-market-capitalization-surges-17-228-billion-2025-2506/
Bastion. (2025, March 20). The state of stablecoins part 1: Market trends, risks, and... Bastion Blog. https://www.bastion.com/blog/the-state-of-stablecoins-March-2025
Statista. (2025, May 19). Market cap ranking of 213 stablecoins on May 19, 2025. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1315474/biggest-stablecoin-in-the-world/
CoinStats. (2025, June 12). Stablecoins reach record market cap of 228 billion in 2025 fueled by increased trading and clearer US regulations. CoinStats News. https://coinstats.app/news/c226a9bb35496de436a423c76020efef46beae5b28a9ea90ca3c56ba87b28416_Stablecoins-Reach-Record-Market-Cap-of-228-Billion-in-2025-Fueled-by-Increased-Trading-and-Clearer-US-Regulations/
Followin. (n.d.). SpaceX uses stablecoin to optimize international payments. Followin. https://followin.io/en/feed/15230554
Johnson, A. (2022, August 10). How does MakerDAO work? Understanding the 'central bank of crypto'. CoinDesk Learn. https://www.coindesk.com/learn/how-does-makerdao-work-understanding-the-central-bank-of-crypto
Cointelegraph. (2025, March 19). Stablecoin users grew 53% in one year: Report. Cointelegraph. https://cointelegraph.com/news/stablecoin-users-53-percent-growth-2025
MEXC. (2025, June 13). Stablecoin surge: Market cap hits record $228B in 2025 amid trading boom and Trump-era clarity. MEXC News. https://www.mexc.com/news/2052
Binance. (2024, December 23). SpaceX utilizes stablecoins for Starlink payments. Binance Square. https://www.binance.com/en/square/post/12-23-2024-spacex-utilizes-stablecoins-for-starlink-payments-17959530761401